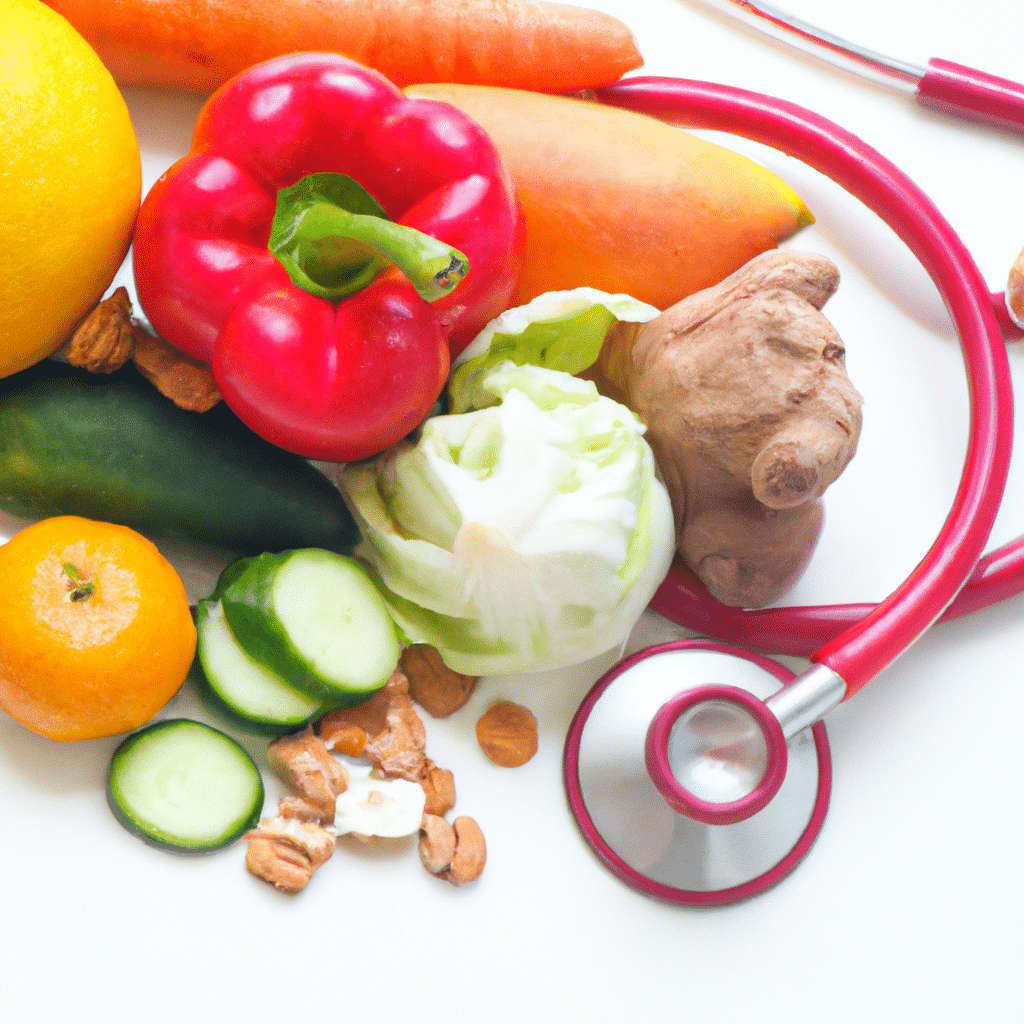
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for a healthy heart. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ultimate diet plan that promotes heart health. By following these guidelines, you will discover the key principles and foods that contribute to a strong cardiovascular system. Whether you are looking to prevent heart disease or improve your overall well-being, this guide will provide you with the essential information to create a healthy diet plan for a healthy heart.
- 1. Introduction
- 1.1. Understanding the importance of a healthy diet for heart health
- 1.2. The link between diet and heart disease
- 1.3. Benefits of following a healthy diet for your heart
- 1.4. Common misconceptions about heart-healthy diets
- 2. Key Components of a Heart-Healthy Diet
- 2.1. Choosing nutrient-rich foods
- 2.2. Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables
- 2.3. Opting for whole grains
- 2.4. Including lean protein sources
- 2.5. Reducing sodium intake
- 3. Foods to Include in a Heart-Healthy Diet
- 3.1. Leafy greens and other vegetables
- 3.2. Berries and other fruits
- 3.3. Nuts and seeds
- 3.4. Fatty fish
- 3.5. Legumes and beans
1. Introduction
Maintaining a healthy heart is crucial for overall well-being and longevity. A key aspect of achieving a healthy heart is following a nutritious diet plan. A healthy diet not only helps in maintaining a healthy weight but also reduces the risk of various heart diseases. This ultimate guide aims to provide you with valuable information and tips on creating a healthy diet plan that is specifically designed to promote a healthy heart. By incorporating these recommendations into your daily routine, you can take a proactive approach towards improving your heart health and living a healthier life.
1.1. Understanding the importance of a healthy diet for heart health
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in maintaining heart health. It provides the necessary nutrients and energy to support the proper functioning of the heart and cardiovascular system. A diet that is rich in nutritious foods can help prevent the development of various heart-related conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and heart disease. In this article, we will explore the importance of a healthy diet for heart health and provide you with a comprehensive guide to creating a diet plan that promotes a healthy heart.
1.2. The link between diet and heart disease
Heart disease is a prevalent health concern worldwide, and it is often associated with poor dietary habits. The link between diet and heart disease has been extensively studied, and research consistently shows that what we eat plays a significant role in the development and prevention of heart-related issues. In fact, a healthy diet plan is considered one of the most effective ways to maintain a healthy heart and reduce the risk of heart disease. This article aims to provide the ultimate guide to a healthy diet plan for a healthy heart, offering valuable insights and recommendations for optimal cardiovascular health.
1.3. Benefits of following a healthy diet for your heart
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of an individual, particularly when it comes to the heart. Following a healthy diet plan can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart diseases and promote a healthy heart. By making smart food choices and incorporating nutrient-rich foods, you can ensure the well-being of your heart and improve your overall quality of life. In this section, we will explore the various benefits of following a healthy diet for your heart.
1.4. Common misconceptions about heart-healthy diets
There are several common misconceptions surrounding heart-healthy diets that need to be addressed. Many people believe that a heart-healthy diet is all about cutting out fats and carbohydrates completely, but this is not entirely true. Another misconception is that all fats are bad for the heart, when in fact, there are healthy fats that are essential for a healthy heart. Additionally, some individuals think that a heart-healthy diet is bland and tasteless, but this is far from the truth. With the right knowledge and guidance, it is possible to follow a delicious and nutritious diet that promotes heart health. In this article, we will debunk these misconceptions and provide you with the ultimate guide to a healthy diet plan for a healthy heart.
2. Key Components of a Heart-Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet is essential for maintaining a healthy heart and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It consists of various key components that provide necessary nutrients and promote heart health. Here are some important elements of a heart-healthy diet:
1. Fruits and vegetables: These should form a significant part of your diet as they are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They help in reducing inflammation and improving heart health.
2. Whole grains: Including whole grains such as oats, brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread in your diet provides essential fiber, minerals, and antioxidants. They help in regulating blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart diseases.
3. Lean proteins: Opt for lean sources of protein such as skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu. These are low in saturated fats and high in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
4. Healthy fats: Incorporate healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil into your diet. These fats help in reducing bad cholesterol levels and maintaining heart health.
5. Low-fat dairy products: Choose low-fat or fat-free dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese. They provide essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D without adding excessive saturated fats.
6. Limit sodium intake: High sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure. It’s important to limit processed and packaged foods, which are often high in sodium. Instead, opt for fresh, homemade meals with minimal added salt.
7. Reduce added sugars: Excessive sugar consumption can increase the risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart diseases. Limit the intake of sugary beverages, desserts, and processed foods that contain added sugars.
8. Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water is essential for overall health, including heart health. It helps in maintaining proper blood circulation and prevents dehydration.
Remember, a heart-healthy diet should be accompanied by regular physical activity and a healthy lifestyle to achieve optimal results for your heart.
2.1. Choosing nutrient-rich foods
Choosing nutrient-rich foods is essential when following a heart-healthy diet. These foods provide the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. The key components of a heart-healthy diet include:
1. Fruits and vegetables: These should form a significant part of your diet. They are low in calories and high in nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants. Aim to include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to ensure you get a range of beneficial nutrients.
2. Whole grains: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and oats instead of refined grains. Whole grains are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals that support heart health.
3. Lean proteins: Choose lean sources of protein such as skinless poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu. These options are low in saturated fats and high in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
4. Healthy fats: Include sources of healthy fats in your diet, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats help reduce bad cholesterol levels and promote heart health.
5. Low-fat dairy products: Opt for low-fat or fat-free dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese. These provide essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D without adding excessive saturated fats.
6. Limit added sugars and salt: Minimize your intake of foods and beverages high in added sugars and sodium. These can contribute to high blood pressure and increase the risk of heart diseases.
By incorporating these key components into your diet, you can prioritize heart health and improve overall well-being.
2.2. Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables
Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables is an essential component of a heart-healthy diet. These nutrient-rich foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote cardiovascular health. When planning your meals, aim to include a colorful array of fruits and vegetables to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients.
Fruits and vegetables are low in calories and high in fiber, making them an excellent choice for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing heart disease. They are also naturally low in sodium and fat, which helps lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of developing high cholesterol levels.
To incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet, start by including them in your breakfast. You can add berries or sliced fruit to your cereal or oatmeal, or blend them into a delicious smoothie. For lunch and dinner, make sure to fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, peppers, and tomatoes. You can also enjoy a side salad or vegetable-based soup.
Snacking on fruits and vegetables is a great way to satisfy your hunger between meals while keeping your heart healthy. Keep a bowl of fresh fruit on your kitchen counter or pack sliced vegetables and hummus as a convenient and nutritious snack. Remember to choose whole fruits and vegetables over processed ones, as they contain more nutrients and are lower in added sugars and unhealthy fats.
In conclusion, incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. These vibrant foods provide an abundance of nutrients and contribute to weight management, blood pressure control, and cholesterol reduction. By making fruits and vegetables a central part of your meals and snacks, you can support your cardiovascular health and enjoy a delicious and nutritious diet.
2.3. Opting for whole grains
Opting for whole grains is a key component of a heart-healthy diet. Whole grains are grains that have not been processed and still contain all three parts of the grain: the bran, germ, and endosperm. These grains are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are all beneficial for heart health.
Including whole grains in your diet can help lower the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke. They are also known to improve cholesterol levels by reducing the levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol in the blood.
Some examples of whole grains include whole wheat, brown rice, oats, quinoa, and barley. These grains can be incorporated into meals in various ways, such as in breakfast cereals, whole grain bread, pasta, and even as a side dish.
When choosing whole grain products, it is important to read the labels carefully. Look for words like ‘whole’ or ‘whole grain’ as the first ingredient, and avoid products that are labeled as ‘refined’ or ‘enriched.’ Additionally, be mindful of portion sizes and opt for whole grains in their most natural form to maximize their health benefits.
In conclusion, opting for whole grains is a simple yet effective way to promote heart health. By including a variety of whole grains in your diet, you can improve your overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart-related conditions.
2.4. Including lean protein sources
Including lean protein sources in your diet is an essential component of a heart-healthy eating plan. Lean protein provides important nutrients while also being low in unhealthy fats. Here are some excellent sources of lean protein to incorporate into your meals:
1. Skinless poultry: Opt for chicken or turkey breast without the skin, as it contains less saturated fat and cholesterol.
2. Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, trout, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
3. Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are not only high in protein but also contain fiber, antioxidants, and other heart-healthy nutrients.
4. Low-fat dairy products: Choose low-fat or fat-free options of milk, yogurt, and cheese to get your protein without the extra saturated fat.
5. Eggs: Despite their cholesterol content, eggs can still be part of a heart-healthy diet when consumed in moderation. Opt for egg whites or egg substitutes for a lower cholesterol option.
Including these lean protein sources in your meals can help promote a healthy heart and overall well-being.
2.5. Reducing sodium intake
Reducing sodium intake is a key component of a heart-healthy diet. Consuming excessive amounts of sodium can contribute to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease. To reduce sodium intake, it is important to minimize the consumption of processed and packaged foods, as they often contain high levels of sodium. Instead, focus on consuming fresh and whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Additionally, reading food labels can help identify hidden sources of sodium in various products. Opt for low-sodium or sodium-free alternatives whenever possible. Cooking meals at home allows for better control over sodium levels, as restaurant and fast food meals tend to be high in sodium. By reducing sodium intake, individuals can effectively promote heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
3. Foods to Include in a Heart-Healthy Diet
A heart-healthy diet plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing heart diseases. Including certain foods in your daily meals can significantly improve your heart health. Here are some essential foods to include in a heart-healthy diet:
1. Fatty Fish: Fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of abnormal heart rhythms.
2. Leafy Green Vegetables: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote heart health.
3. Berries: Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are high in antioxidants and can help reduce inflammation and improve blood flow.
4. Whole Grains: Including whole grains like oats, brown rice, and whole wheat bread in your diet can lower the risk of heart disease by reducing cholesterol levels.
5. Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are all excellent sources of heart-healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants.
6. Olive Oil: Using olive oil as a primary source of fat in cooking can help lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
7. Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich in fiber, protein, and other essential nutrients that contribute to heart health.
8. Avocado: Avocados are packed with monounsaturated fats, potassium, and fiber, which can help lower bad cholesterol and maintain heart health.
9. Tomatoes: Tomatoes are an excellent source of lycopene, an antioxidant that can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
10. Dark Chocolate: Consuming moderate amounts of dark chocolate with a high cocoa content can improve heart health due to its antioxidant properties.
Remember, incorporating these heart-healthy foods into your diet is just one part of maintaining a healthy heart. It is also crucial to limit the intake of foods high in saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars.
3.1. Leafy greens and other vegetables
Including leafy greens and other vegetables in your diet is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. These nutrient-rich foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help reduce the risk of heart disease. Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are particularly beneficial due to their high levels of fiber, potassium, and folate. Fiber aids in lowering cholesterol levels, while potassium helps regulate blood pressure. Folate plays a key role in preventing the buildup of homocysteine, an amino acid that can damage blood vessels.
Other vegetables such as broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers also offer heart-healthy benefits. Broccoli contains sulforaphane, a compound that may help protect against heart disease by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Carrots are rich in beta-carotene, which is converted into vitamin A in the body and can promote heart health. Bell peppers are an excellent source of antioxidants, including vitamin C, which can help protect against heart disease.
Incorporating leafy greens and other vegetables into your diet can be as simple as adding them to salads, stir-fries, or smoothies. Aim to include a variety of colors and types to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients. By prioritizing these heart-healthy foods, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy diet plan for a healthy heart.
3.2. Berries and other fruits
Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, are excellent choices to include in a heart-healthy diet. These vibrant fruits are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber, which are beneficial for cardiovascular health. Berries have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease by improving cholesterol levels and reducing blood pressure. They also have anti-inflammatory properties that help protect against the development of plaque in the arteries. Additionally, berries are low in calories and high in natural sugars, making them a satisfying and nutritious snack. To reap the maximum benefits, it is recommended to consume a variety of berries regularly. Other fruits like apples, oranges, and pears are also great options for a heart-healthy diet. They are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and can help lower the risk of heart disease when included as part of a balanced eating plan.
3.3. Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are excellent additions to a heart-healthy diet plan. Packed with essential nutrients, they offer numerous health benefits. Nuts like almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are rich in heart-healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants, which can help reduce LDL cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Seeds such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and sunflower seeds are also great sources of omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and plant-based protein. Including a variety of nuts and seeds in your diet can promote heart health and lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. They can be enjoyed as a snack, added to salads, or incorporated into various recipes to enhance both taste and nutritional value.
3.4. Fatty fish
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, should be included in a heart-healthy diet. These types of fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to provide numerous benefits for heart health. Omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation, decrease triglyceride levels, lower blood pressure, and prevent the formation of blood clots. Additionally, consuming fatty fish regularly may help improve cholesterol levels by increasing HDL (good) cholesterol and reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol. Including fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week can significantly contribute to a healthy heart and overall well-being.
3.5. Legumes and beans
Including legumes and beans in your diet is highly beneficial for maintaining a healthy heart. Legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans, are excellent sources of plant-based protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. Consuming legumes regularly can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Beans, including kidney beans, navy beans, and pinto beans, are also rich in fiber and contain significant amounts of antioxidants. These properties make them effective in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, which are known risk factors for heart disease.
Incorporating legumes and beans into your meals is relatively easy. You can add them to salads, soups, stews, or use them as a base for vegetarian dishes. They are versatile, filling, and provide a satisfying texture. Moreover, legumes and beans are budget-friendly and readily available, making them an ideal choice for a heart-healthy diet.
By including legumes and beans in your diet, you can reap the numerous health benefits they offer and promote a healthy heart.
Conclusion
In conclusion, following a healthy diet plan is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help reduce the risk of heart diseases. Additionally, limiting the consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive sodium is essential for heart health. With proper nutrition and lifestyle choices, individuals can ensure a strong and healthy heart for a lifetime.


